逍遥云's Blog
努力做好自己!
单向链表反转
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 | #include <stdlib.h>struct List { int index; struct List *next;};void create_list(struct List **list, int len){ *list = (struct List *) malloc(sizeof(struct List)); (*list)->next = NULL; struct List* p; while(len) { p = (struct List*) malloc(sizeof(struct List)); p->index = len--; p->next = (*list)->next; (*list)->next = p; }}void reverse_list(struct List **list){ struct List *next, *prev, *node; prev = NULL; node = *list; while(node) { next = node->next; if(next == NULL) *list = node; node->next = prev; prev = node; node = next; }}void destory_list(struct List *list){ if(list->next) destory_list(list->next); free(list); list->index = 0; list->next = NULL;}int main(void){ struct List *data; create_list(&data, 20); reverse_list(&data); destory_list(data); return 0;} |
东抄抄, 西抄抄, 写了个大概, 玩着玩着都会感觉混淆了.
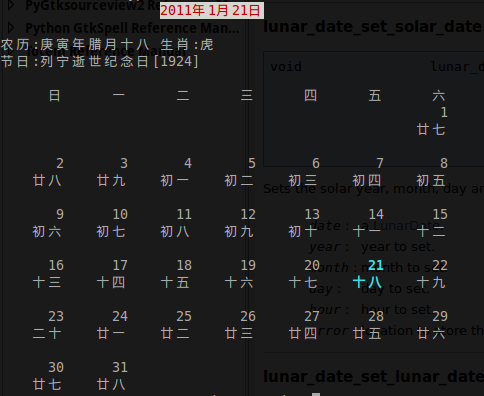
一个查看阴历的小工具
接着上一篇liblunar的日历bug问题,这里写了一个查询月份的工具,代码比较简陋
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 | /* * author:pallover#gmail.com * website: http://pallove.is-programmer.com/ */#include <lunar/lunar.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>#include <time.h>int str2int(const char *str){ int n = 0; while(*str >= '0' && *str <= '9') { n = n * 10 + (*str - '0'); str++; } return n;}int get_weekday(int year, int month, int day){ int m = month; if(m == 1) { m = 13; year -= 1; } else if(m == 2) { m = 14; year -= 1; } int c = year / 100; int y = year % 100; int d = day; return (((c >> 2) - (c << 1) + y + (y >> 2) + (13 * (m + 1) / 5) + d - 1) % 7 + 7) % 7;}int get_mdays(int year, int month){ switch(month) { case 1: case 3: case 5: case 7: case 8: case 10: case 12: return 31; case 4: case 6: case 9: case 11: return 30; case 2: if(!(year % 4) && year % 100 || !(year % 400)) return 29; else return 28; }}int main(int argc, char *argv[]){ struct tm *tm_ptr; time_t the_time; (void) time(&the_time); tm_ptr = localtime(&the_time); int nyear = 0, nmonth = 1, nday = 1; if(argc > 1) { nyear = str2int(argv[1]); if(nyear <= 1900) nyear = tm_ptr->tm_year + 1900; if(argc > 2) { nmonth = str2int(argv[2]); if(nmonth < 1) nmonth = 1; if(argc > 3) { nday = str2int(argv[3]); if(nday < 1) nday = 1; } } } else { nyear = tm_ptr->tm_year + 1900; nmonth = tm_ptr->tm_mon + 1; nday = tm_ptr->tm_mday; printf("%d, %d, %d\n", nyear, nmonth, nday); } lunar_init(&argc, &argv); LunarDate *lunar_date = lunar_date_new(); lunar_date_set_solar_date(lunar_date, nyear, nmonth, nday, 1, NULL); gchar *str = lunar_date_strftime(lunar_date, "%(NIAN)年%(YUE)月%(RI) 生肖:%(shengxiao) \n节日:%(jieri)"); printf("\n%*s%s%d年%d月%d日%s\n\n", 20, "", "\033[47m\033[31m", nyear, nmonth, nday, "\033[0m"); printf("农历:%s\n\n", str); char *weekday = "日一二三四五六"; char ch[4]; while(*weekday){ strncpy(ch, weekday, 3); ch[3] = 0; weekday += 3; printf("%*s%2s", 6, "", ch); } int i = 1, line, nlen, n, firstwday, endline = 0; int nmdays = get_mdays(nyear, nmonth); firstwday = get_weekday(nyear, nmonth, 1); printf("\n"); line = 7 - firstwday; while(nmdays > 0) { if(line % 7 && !endline) printf("%*s", firstwday << 3, ""); for(nlen = 0; nlen < line; nlen++, i++) { n = get_weekday(nyear, nmonth, i); printf("%*s%s%2d%s", 6, "", ((i == nday) ? "\033[36m\033[1m" : ""), i, ((i == nday) ? "\033[0m" : "")); } i -= line; if(n == 6 || endline) { printf("\n"); } if(line % 7 && !endline) printf("%*s", firstwday << 3, ""); for(nlen = 0; nlen < line; nlen++, i++) { lunar_date_set_solar_date(lunar_date, nyear, nmonth, i, 0, NULL); printf("%*s%s%4s%s", 4, "", ((i == nday) ? "\033[36m\033[1m" : ""), lunar_date_strftime(lunar_date, "%(RI)"), ((i == nday) ? "\033[0m" : "")); } if(n == 6 || endline) { printf("\n\n"); } nmdays -= line; line = (nmdays >= 7) ? 7 : nmdays % 7, endline = 1; } lunar_date_free(lunar_date); exit(0);} |
可以传入0-3个自己想查询有效参数(年,月,日),如不输入,则默认为本地日期。
liblunar的调用节日的bug
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 | if (strstr(format, "%(jieri)") != NULL){ gchar bufs[128]; gchar *tmp; tmp = lunar_date_get_jieri(date, " "); if (*tmp) { g_utf8_strncpy(bufs, tmp, g_utf8_strlen(tmp, 128)); } /*if (strstr(tmp, " " ) != NULL) { char** buf = g_strsplit(tmp, " ", -1); if (g_utf8_validate(*buf, -1, NULL)) g_utf8_strncpy(bufs, *buf, 3); else { strncpy(bufs, *buf, 4); bufs[4]= '\0'; } g_strfreev(buf); } else { if (g_utf8_validate(tmp, -1, NULL)) g_utf8_strncpy(bufs, tmp, 3); else { strncpy(bufs, tmp, 4); bufs[4]= '\0'; } }*/ g_free(tmp); str = g_string_replace(str, "%(jieri)", bufs, -1);} |
好吧,本意是要拆分开然后再组在一起,却写的莫名其妙的,应该用循环也没用,就改了下。这下可以显示全了。
测试的代码为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | #include <lunar/lunar.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>int main(int argc, char *argv[]){ //g_type_init(); 这句我扔到lunar_init函数里面去了。 lunar_init(&argc, &argv); LunarDate *lunar_date = lunar_date_new(); lunar_date_set_solar_date(lunar_date, 2011, 10, 28, 1, NULL); gchar *str = lunar_date_strftime(lunar_date, "%(NIAN)年%(YUE)月%(RI)日%(SHI)时 生肖:%(shengxiao) 节日:%(jieri)"); printf("out str:%s", str); lunar_date_free(lunar_date); exit(0);} |
utf-8字符窜对应的辅助函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 | intutf8_char_size(const unsigned char c){ if(c < 0x80) return 1; if((c & 0xc0) == 0x80) return 0; int mask = 0x80; int num = 0; while(mask & c) { ++num; mask >>= 1; } return num;}intutf8_len(const char *utf8){ const unsigned char *input = (const unsigned char *)utf8; int count = 0; while(*input) { while((*input & 0xc0) == 0x80) ++input; count++; input++; }; return count;}intutf8_char_at(const char *utf8, int index){ const unsigned char *input = (const unsigned char *)utf8; int count = 0; while(*input) { if(count == index) return input - (const unsigned char *)utf8; input += utf8_char_size(*input); count++; }; return -1;} |
int utf8_char_size(const unsigned char c) //取得utf-8字符的长度.
例子: char *str="中文";utf8_char_size(*str)=3;utf8_char_size(*++str)=0
int utf8_len(const char *utf8) //取得字符窜的长度,类似wcslen(wchar_t)
例子: utf8_len("hello你好,world") = 17
int utf8_char_at(const char *utf8, int index) // 取得utf-8字符窜真实地址偏移值
例子:utf8_char_at("hello你好,world", 7) = 11
C替换函数
先前在百度空间里帖了一个函数,很乱也蛮烂的
http://hi.baidu.com/pallove/blog/item/ea3c0b469c4bf0076a63e53e.html
早上使用strstr函数再写了一个,一下感觉清爽多了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | #include <string.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>char* replace(const char *src, const char *from, const char *to, char *dest){ int idx = 0; char *find; while(1) { if(find = strstr(src, from)) { idx = find - src; strncat(dest, src, idx); strncat(dest, to, strlen(to)); src += idx + strlen(from); } else { strncat(dest, src, strlen(src)); break; } } return dest;}int main(){ char *dest = malloc(1024); strcpy(dest, "result:"); printf("%s\n", replace("hello, abcabctestasdlfklasdjabc ldsafabc", "abc", "123", dest)); exit(0);} |