逍遥云's Blog
努力做好自己!
过河问题(lua版)
再次写这篇博文,也算是一次回归吧。许久不写文字,发现说话也不太顺溜了,就此以这段开码开个头吧。
题目:一老人带一条狗,同夫妻二人及男孩女孩各俩(七人加一条狗)由河左岸到右岸,有渡船一只,在如下规则下,问多少次方可全部过河?
规则:1. 可撑船有三人:老人,丈夫,妻子。2. 渡船每次至多携带两位,但至少有一位撑船者。3. 狗在老人的掌控之下才不会伤及他人,但可独处。4. 丈夫喜男孩而不喜女孩,故男孩不可与妻子独处。5. 妻子喜欢女孩而不喜男孩,故女孩不可与丈夫独处
Linux下一个有趣的文件夹软链接
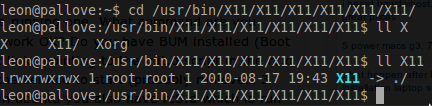
当你cd了半天,你肯定在想,我靠,是不是中毒了,谁TMD搞的这么多层级的文件夹,当你ls一看,你会说句: 我靠!
另:已经再工作了,虽然不是自己想要的事,但毕竟还是做程序。
SDL开发的简易版'宝石'迷情
爱情与事业相冲突,我选择了爱情,也可以说是家庭与事业冲突吧,毕竟也是结了婚准备小孩的人了,这也导致了我工作难稳定下来,当然自己与运气也有很大关系吧,谁叫我是一个不太认输的人呢?要不然放着自己搞了几年了flash程序,鬼使神差地想做linux下的开发,导致工作一直没有着落,就这样过了好几个月,权当是休息了。国内的企业功绩心太强了,招人比较看重作品,归纳为看重“整合”能力,也就是说不管你怎么样,你独立整一个东西出来,这个就做为评价的标准,有点粗犷吧,这根每一个以利益为目的的企业理念相同。闲话完了,归入正题。
SDL也断断续续看了蛮久的时间了,看教程,看文档,ubuntu下vim+gdb的开发方式的确比vs费事,但是既然选择了linux,还有什么好抱怨的,关键的问题还是在你的开发过程中,总是要中断去看看别的知识,如:把sdl的tags加到当前环境中,把gdb整合到7.2版的vim中,看翻看gdb资料,写好代码要再回忆下makefile是如何写的,网上查询资料被墙还要开个vpn等等,东一转西一转,蛮磨时间的。
昨天就在家中一边看着《神探狄仁杰3》一边就在vim里面捣鼓着,写了这样一个小游戏。

只所以把宝石打了引号,我想不说大家也明白吧, XD
这里是源码+可执行文件,我把库做成静态的了。没有库的朋友不必担心。
/user_files/pallove/File/ball_game.tar.gz
玩法:找3个及以上一样的球使劲是用鼠标戳吧。
bash+expect来处理下载完关机
昨天在用ff从tgbus上下载几个psp游戏,然后在想定个时在什么时候关机
sudo shutdown -h +320
但是一想,如果这破电信的网速不好,那岂不是白搞了(不知115是否能断点续传),然后就想到搞个下载完关机的sh脚本。
这里sh脚本我就不说了,思路是:
while循环
sleep两秒
如果测试没有以part结尾的文件名的话
关机
想到这些我就写下了这样的东东
#!/bin/bash
while $(sleep 2);
do
if [ ! -f *.part ]; then # 测试当前目录下有无firefox未下载完的文件
sudo shutdown -h now
fi
done
后来觉得有一问题,就是要管理员的密码。进而就想到了使用expect, 然后就把shutdown那句放入了命名为power-off.expect文件中。
#!/usr/bin/expect set timeout 60 spawn sudo shutdown -h +1 # 推迟1分钟,以防文件还未写完。 expect "leon:" # 这句是猜测执行上段命令回显的最后几个字符,大概就是"password for user:"或 "Password:"或"密码:" send "yourpassword\r" interact
注意:这里的power-off.expect里面你的密码就是明文了,一定要注意权限,我是直接700了(即同组与其它组无读,无写,无执行权限)。
然后,将power-off.expect放入要调用的执行脚本,即
#!/bin/bash
while $(sleep 2);
do
if [ ! -f *.part ]; then # 测试当前目录下有无firefox未下载完的文件
./power-off.expect
fi
done
c写的插入排序
本来再想,写这样的初级代码发还是不发,后来还是帖了出来。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
static void genIntArray(int *arr, int nlen)
{
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
while(nlen--) *arr++ = rand() % 300 + 5;
}
static void insertion_sort(int *arr, int nlen, int (*sort_func)(int, int))
{
int i, j, tmp;
for( i = 1; i < nlen; i++) {
j = i;
while( j > 0 && sort_func(arr[j], arr[j - 1])) {
tmp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j - 1];
arr[j - 1] = tmp;
--j;
}
}
}
static int lower_sort(int num1, int num2)
{
return num1 > num2;
}
static int upper_sort(int num1, int num2)
{
return num1 < num2;
}
static void printArray(int *arr, int nlen)
{
printf("[");
while(--nlen) printf("%d, ", *arr++);
printf("%d]\n", *arr);
}
int main(void)
{
int len = 10;
int arr[len];
genIntArray(arr, len);
printf("before sort:");
printArray(arr, len);
insertion_sort(arr, len, lower_sort);
printf("after lower sort:");
printArray(arr, len);
insertion_sort(arr, len, upper_sort);
printf("after upper sort:");
printArray(arr, len);
return 0;
}
后记:在编程中,时常把一个函数当做参数传来传去,这也是编程里面比较有意思的事情。
单向链表反转
#include <stdlib.h>
struct List {
int index;
struct List *next;
};
void create_list(struct List **list, int len)
{
*list = (struct List *) malloc(sizeof(struct List));
(*list)->next = NULL;
struct List* p;
while(len)
{
p = (struct List*) malloc(sizeof(struct List));
p->index = len--;
p->next = (*list)->next;
(*list)->next = p;
}
}
void reverse_list(struct List **list)
{
struct List *next, *prev, *node;
prev = NULL;
node = *list;
while(node) {
next = node->next;
if(next == NULL) *list = node;
node->next = prev;
prev = node;
node = next;
}
}
void destory_list(struct List *list)
{
if(list->next) destory_list(list->next);
free(list);
list->index = 0;
list->next = NULL;
}
int main(void)
{
struct List *data;
create_list(&data, 20);
reverse_list(&data);
destory_list(data);
return 0;
}
东抄抄, 西抄抄, 写了个大概, 玩着玩着都会感觉混淆了.
一个查看阴历的小工具
接着上一篇liblunar的日历bug问题,这里写了一个查询月份的工具,代码比较简陋
/*
* author:pallover#gmail.com
* website: http://pallove.is-programmer.com/
*/
#include <lunar/lunar.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
int str2int(const char *str)
{
int n = 0;
while(*str >= '0' && *str <= '9')
{
n = n * 10 + (*str - '0');
str++;
}
return n;
}
int get_weekday(int year, int month, int day)
{
int m = month;
if(m == 1) {
m = 13;
year -= 1;
}
else if(m == 2) {
m = 14;
year -= 1;
}
int c = year / 100;
int y = year % 100;
int d = day;
return (((c >> 2) - (c << 1) + y + (y >> 2) + (13 * (m + 1) / 5) + d - 1) % 7 + 7) % 7;
}
int get_mdays(int year, int month)
{
switch(month) {
case 1:
case 3:
case 5:
case 7:
case 8:
case 10:
case 12:
return 31;
case 4:
case 6:
case 9:
case 11:
return 30;
case 2:
if(!(year % 4) && year % 100 || !(year % 400))
return 29;
else
return 28;
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct tm *tm_ptr;
time_t the_time;
(void) time(&the_time);
tm_ptr = localtime(&the_time);
int nyear = 0, nmonth = 1, nday = 1;
if(argc > 1) {
nyear = str2int(argv[1]);
if(nyear <= 1900) nyear = tm_ptr->tm_year + 1900;
if(argc > 2) {
nmonth = str2int(argv[2]);
if(nmonth < 1) nmonth = 1;
if(argc > 3) {
nday = str2int(argv[3]);
if(nday < 1) nday = 1;
}
}
}
else {
nyear = tm_ptr->tm_year + 1900;
nmonth = tm_ptr->tm_mon + 1;
nday = tm_ptr->tm_mday;
printf("%d, %d, %d\n", nyear, nmonth, nday);
}
lunar_init(&argc, &argv);
LunarDate *lunar_date = lunar_date_new();
lunar_date_set_solar_date(lunar_date, nyear, nmonth, nday, 1, NULL);
gchar *str = lunar_date_strftime(lunar_date, "%(NIAN)年%(YUE)月%(RI) 生肖:%(shengxiao) \n节日:%(jieri)");
printf("\n%*s%s%d年%d月%d日%s\n\n", 20, "", "\033[47m\033[31m", nyear, nmonth, nday, "\033[0m");
printf("农历:%s\n\n", str);
char *weekday = "日一二三四五六";
char ch[4];
while(*weekday){
strncpy(ch, weekday, 3);
ch[3] = 0;
weekday += 3;
printf("%*s%2s", 6, "", ch);
}
int i = 1, line, nlen, n, firstwday, endline = 0;
int nmdays = get_mdays(nyear, nmonth);
firstwday = get_weekday(nyear, nmonth, 1);
printf("\n");
line = 7 - firstwday;
while(nmdays > 0)
{
if(line % 7 && !endline)
printf("%*s", firstwday << 3, "");
for(nlen = 0; nlen < line; nlen++, i++) {
n = get_weekday(nyear, nmonth, i);
printf("%*s%s%2d%s", 6, "", ((i == nday) ? "\033[36m\033[1m" : ""), i, ((i == nday) ? "\033[0m" : ""));
}
i -= line;
if(n == 6 || endline) {
printf("\n");
}
if(line % 7 && !endline)
printf("%*s", firstwday << 3, "");
for(nlen = 0; nlen < line; nlen++, i++) {
lunar_date_set_solar_date(lunar_date, nyear, nmonth, i, 0, NULL);
printf("%*s%s%4s%s", 4, "", ((i == nday) ? "\033[36m\033[1m" : ""), lunar_date_strftime(lunar_date, "%(RI)"), ((i == nday) ? "\033[0m" : ""));
}
if(n == 6 || endline) {
printf("\n\n");
}
nmdays -= line;
line = (nmdays >= 7) ? 7 : nmdays % 7, endline = 1;
}
lunar_date_free(lunar_date);
exit(0);
}
可以传入0-3个自己想查询有效参数(年,月,日),如不输入,则默认为本地日期。
liblunar的调用节日的bug
if (strstr(format, "%(jieri)") != NULL)
{
gchar bufs[128];
gchar *tmp;
tmp = lunar_date_get_jieri(date, " ");
if (*tmp)
{
g_utf8_strncpy(bufs, tmp, g_utf8_strlen(tmp, 128));
}
/*if (strstr(tmp, " " ) != NULL)
{
char** buf = g_strsplit(tmp, " ", -1);
if (g_utf8_validate(*buf, -1, NULL))
g_utf8_strncpy(bufs, *buf, 3);
else
{
strncpy(bufs, *buf, 4);
bufs[4]= '\0';
}
g_strfreev(buf);
}
else
{
if (g_utf8_validate(tmp, -1, NULL))
g_utf8_strncpy(bufs, tmp, 3);
else
{
strncpy(bufs, tmp, 4);
bufs[4]= '\0';
}
}*/
g_free(tmp);
str = g_string_replace(str, "%(jieri)", bufs, -1);
}
好吧,本意是要拆分开然后再组在一起,却写的莫名其妙的,应该用循环也没用,就改了下。这下可以显示全了。
测试的代码为:
#include <lunar/lunar.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//g_type_init(); 这句我扔到lunar_init函数里面去了。
lunar_init(&argc, &argv);
LunarDate *lunar_date = lunar_date_new();
lunar_date_set_solar_date(lunar_date, 2011, 10, 28, 1, NULL);
gchar *str = lunar_date_strftime(lunar_date, "%(NIAN)年%(YUE)月%(RI)日%(SHI)时 生肖:%(shengxiao) 节日:%(jieri)");
printf("out str:%s", str);
lunar_date_free(lunar_date);
exit(0);
}
union的妙用
先前看了SDL的SDL_Event, 不大明白其中的用法,后来翻了翻书中关于union的用法,再则看到了云风的这篇文章C 语言中统一的函数指针, 就写了一个不成文的例子, 把union作为函数的参数传递, 可以将两个毫不相干的不同类型的结构数据粘合在一起, 的确很有意思.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef enum bool {false, true} bool;
typedef struct Number {
unsigned char type;
unsigned int num;
bool sign;
} Number;
typedef struct OP {
unsigned char type;
char ch;
} OP;
typedef union Button {
unsigned char type;
Number num;
OP op;
} Button;
void printNum(int num)
{
printf("Print Number:%d\n", num);
}
void printOP(char op)
{
printf("Print Op:%c\n", op);
}
void cal(Button p)
{
switch(p.type)
{
case 1:
printNum(p.num.num * ((p.num.sign) ? 1 : -1));
break;
case 2:
printOP(p.op.ch);
break;
}
}
int main()
{
Button p1;
p1.num = (Number) {1, 9, false};
cal(p1);
p1.op = (OP) {2, '='};
cal(p1);
exit(0);
}
这里要注意结构体的第一个字段一定要与union的第一个字符对应起来, 至于为什么, 去翻看union用法吧...
utf-8字符窜对应的辅助函数
int
utf8_char_size(const unsigned char c)
{
if(c < 0x80) return 1;
if((c & 0xc0) == 0x80) return 0;
int mask = 0x80;
int num = 0;
while(mask & c)
{
++num;
mask >>= 1;
}
return num;
}
int
utf8_len(const char *utf8)
{
const unsigned char *input = (const unsigned char *)utf8;
int count = 0;
while(*input) {
while((*input & 0xc0) == 0x80)
++input;
count++;
input++;
};
return count;
}
int
utf8_char_at(const char *utf8, int index)
{
const unsigned char *input = (const unsigned char *)utf8;
int count = 0;
while(*input) {
if(count == index) return input - (const unsigned char *)utf8;
input += utf8_char_size(*input);
count++;
};
return -1;
}
int utf8_char_size(const unsigned char c) //取得utf-8字符的长度.
例子: char *str="中文";utf8_char_size(*str)=3;utf8_char_size(*++str)=0
int utf8_len(const char *utf8) //取得字符窜的长度,类似wcslen(wchar_t)
例子: utf8_len("hello你好,world") = 17
int utf8_char_at(const char *utf8, int index) // 取得utf-8字符窜真实地址偏移值
例子:utf8_char_at("hello你好,world", 7) = 11